How Medical Cannabis Can Help Arthritis Patients
More than 31 million people in America suffer from arthritis, a painful disease that causes inflammation, pain, and swelling to joints in the body. This limits movement and causes physical pain along with frustration and anxiety that comes along with chronic suffering. There are two types of arthritis: osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Both are serious and both can be treated with medical cannabis.
- Osteoarthritis is known as “arthritis of the bones” because it is caused by the wearing of cartilage (flexible tissue at the ends of bones) in mostly elderly skeletal systems. Osteoarthritis is generally caused by many years of wear and tear on the skeletal-muscular system. In some cases, however, osteoarthritis may manifest as chronic inflammation in the joints from injury. Osteoarthritis is more common than Rheumatoid Arthritis and currently affects more than 10 million people worldwide. There are no drugs to modify or cure this condition, and the treatment approach is generally focused on pain control through prescription painkillers such as opiates, APAP, or other painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs can create side effects as they treat pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the synovial membranes in the body, which facilitate joint maneuverability. As this wears away, cartilage is also destroyed and bones become eroded, causing a number of symptoms, mainly pain, and limited movement in the joints. RA can afflict anyone at any age, but it’s most common in the elderly.
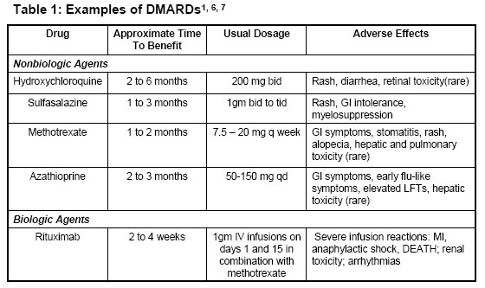
Arthritis patients are often treated with medications such as NSAIDs, steroids, nonacetylated salicylates, DMARDs, and prescription analgesics as well as non-prescription analgesics. These drugs often have side effects such as nausea, pain, and other non-symptomatic health issues. Some of the drugs commonly used to treat arthritis can even cause tinnitus (constant ringing of the ears,) or even complete loss of hearing. Cannabis presents a solution to control the negative side effects of these medicines, or even eliminate the need for some of them for some patients.\
As arthritis patient ages, bone health becomes even more crucial to their well-being than it did previously. The skeletal system is dynamic, constantly re-modeling itself and undergoing changes. Natural skeletal movement and reconstruction can lead to the destruction and degradation of connective bone tissues such as the synovial joints, causing pain, wearing down bones, and leading to reduced mobility of the joints. Cannabis is a treatment option that is protective of the skeletal system because medical cannabis has shown to be positive for maintaining bone health, as well as controlling pain. In the past, researchers from Tel Aviv had found that the skeleton is regulated by cannabinoids and that bone formation is stimulated by cannabinoids and their receptors throughout the body, meaning that cannabis is inhibiting bone loss while managing pain and other symptoms.
Cannabidiol, or CBD, has been proven to stimulate bone growth as well as provide protection to the other bones in the skeletal system. According to a study published in the Journal of Bone Health and Medicine by Dr. Yankel Gabet, CBD alone promotes “markedly advanced” healing in broken bones by enhancing and speeding up the maturation of the collagenous matrix in the bone, a microstructure that provides the basis for mineralization of new bone tissue. With CBD therapy, according to Dr. Gabet’s study, the broken bones will not only heal faster but be harder to break than a bone left untreated with CBD.
Besides just healing bones, cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are metabolized in the body and turned into healing cannabinoid variants/metabolites. These metabolites are believed to significantly relieve inflammation, pain, and other musculoskeletal symptoms of arthritis.
Using cannabis to treat arthritis is a beneficial step in the healing and treatment process of both types of arthritis. Since cannabis not only heals bone damage but also controls pain and alleviates tension, it is a good option for arthritics that deal with the suffering that the disease causes and want to find an alternative method of treatment.
As always, we suggest you discuss your treatment options with your physician.
If you’re a medical marijuana patient, view our menu for cannabis products.
Resources used in the writing of this article:
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19634029
- http://www.safeaccessnow.org/arthritis_booklet#reference
- http://www.livescience.com/51701-marijuana-bones-healing-fractures.html
What is the Cannabinoid CBG?
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is a cannabinoid found in cannabis sativa plants and extracts. CBG was originally discovered by scientists while working with hashish in 1965, which lead researchers to believe it was a constituent of hash until 1975, when researchers found that the acid form of CBG (CBGA) occurs naturally as the first cannabinoid to form in a new cannabis plant. CBGA is then turned into other cannabinoids such as THCA, CBDA, or CBCA through degradation and reconstruction with enzymes.
Since CBG is essentially the building blocks for other cannabinoids, many scientists consider it a “stem cell” like cannabinoid. It’s the essential precursor for all of the cannabinoids that create the healing and psychoactive effects of cannabis.
(Photo credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/87/CBG-type_cannabinoid.png))
Scientists have discovered many uses for CBG, all medicinally beneficial. In January this year, researchers in Spain discovered that CBG has neuro protective effects in mice with Huntington’s disease. Huntington’s disease is characterized by nerve degeneration in the brain, and CBG was shown to protect the nerves and slow down damage. CBG also showed promise as a potential treatment for colon cancer, as it was shown in a study that CBG slows down the progression of colon cancer in mice. CBG has also been shown to have potential as an antidepressant, for the treatment of psoriasis, and as an analgesic.
Since CBG has so many possible medical applications, why hasn’t anyone harnessed the power of CBG yet? Simply put, it’s not an abundant cannabinoid. It exists in levels around 1% or less in most plants, and is not easy to extract and isolate without a serious lab, however, some strains do show potential to be bred with high CBG output. Narrow leafed strains from the geographic area of India are supposedly higher in CBG, but it’s not a confirmed discovery. Scientists also have found that around the 6 week mark of flowering, CBG (not CBGa) can be found in higher levels than any other week of flowering. CBG’s future is bright, but before harnessing the raw power of cannabinoid stem cells, there must be more research done on how to properly harness its power. You can always learn more about CBG and other products with SWC Arizona located in Tempe, AZ.
(Photo credit: leafly.com)
Resources used in the writing of this article:
Cancer and Cannabis: Updates from NCI
 The National Cancer Institute, or NCI, has recently updated language on their website recognizing the potential value of cannabis in treating cancer and related symptoms. This is the first time a government run organization has outwardly admitted that there’s evidence showing that cannabis and cannabinoids can be used to fight the disease. Before, there was nothing stating that research had been done on the anti-tumor possibilities of cannabis.
The NCI website states “The potential benefits of medicinal Cannabis for people living with cancer include antiemetic effects, appetite stimulation, pain relief, and improved sleep. Although few relevant surveys of practice patterns exist, it appears that physicians caring for cancer patients in the United States who recommend medicinal Cannabis predominantly do so for symptom management.”
The NCI website also states that “Cannabis has been shown to kill cancer cells in the laboratory (see question 6).” “Question 6” is a page showing whether preclinical studies with cannabinoids had been conducted, and what they were conducted on.
While this may not make any quick changes to medical cannabis laws, it is a step in the right direction. We are looking forward to continued research to help scientists learn more about the medical benefits of marijuana for cancer patients.
Resources used in writing this post:
The National Cancer Institute, or NCI, has recently updated language on their website recognizing the potential value of cannabis in treating cancer and related symptoms. This is the first time a government run organization has outwardly admitted that there’s evidence showing that cannabis and cannabinoids can be used to fight the disease. Before, there was nothing stating that research had been done on the anti-tumor possibilities of cannabis.
The NCI website states “The potential benefits of medicinal Cannabis for people living with cancer include antiemetic effects, appetite stimulation, pain relief, and improved sleep. Although few relevant surveys of practice patterns exist, it appears that physicians caring for cancer patients in the United States who recommend medicinal Cannabis predominantly do so for symptom management.”
The NCI website also states that “Cannabis has been shown to kill cancer cells in the laboratory (see question 6).” “Question 6” is a page showing whether preclinical studies with cannabinoids had been conducted, and what they were conducted on.
While this may not make any quick changes to medical cannabis laws, it is a step in the right direction. We are looking forward to continued research to help scientists learn more about the medical benefits of marijuana for cancer patients.
Resources used in writing this post:
- http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/patient/cannabis-pdq
- http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/patient/cannabis-pdq/#link/_13
- http://marijuanapolitics.com/cancer-gov-forgot-say-cannabis/
Featured MMJ Strain: Fire OG
 (Photo credit: http://cdn.shopify.com)
Fire OG is a hybrid strain, made of a cross between San Fernando Valley (SFV) OG Kush and OG Kush, both the same strain technically, but different phenotypes. According to leafly.com’s guide to cannabis genetics, “The plant’s genetic makeup, also called a genotype, acts as a blueprint for growth: it allows a spectrum of physical possibilities, but it is up to the environment to induce these characteristics. The physical expression of a genotype is referred to as a phenotype, which is simply defined as the traits that the environment pulls out from the plant’s genetic code. Everything from color, shape, smell, and resin production are affected by the environment.”
The terpenes in Fire OG are similar to that of most OG: Gas, Skunk, Kush, and lemons/fruit. Fire OG has a staggeringly high level of Beta-myrcene on average, a terpene shared with mangos, giving the buds a nice fruity undertone that works perfectly with the pungent fuel-y overtones. Typically, Fire OG is a dense herb, following the almost geometric calyx structure that most OG’s do. Intertwined between these calyxes are tons of red hairs, which are thought to be the inspiration for the name “Fire OG.”
(Photo credit: http://cdn.shopify.com)
Fire OG is a hybrid strain, made of a cross between San Fernando Valley (SFV) OG Kush and OG Kush, both the same strain technically, but different phenotypes. According to leafly.com’s guide to cannabis genetics, “The plant’s genetic makeup, also called a genotype, acts as a blueprint for growth: it allows a spectrum of physical possibilities, but it is up to the environment to induce these characteristics. The physical expression of a genotype is referred to as a phenotype, which is simply defined as the traits that the environment pulls out from the plant’s genetic code. Everything from color, shape, smell, and resin production are affected by the environment.”
The terpenes in Fire OG are similar to that of most OG: Gas, Skunk, Kush, and lemons/fruit. Fire OG has a staggeringly high level of Beta-myrcene on average, a terpene shared with mangos, giving the buds a nice fruity undertone that works perfectly with the pungent fuel-y overtones. Typically, Fire OG is a dense herb, following the almost geometric calyx structure that most OG’s do. Intertwined between these calyxes are tons of red hairs, which are thought to be the inspiration for the name “Fire OG.”